
The Internet protocol suite (commonly known as TCP/IP71) is the set of communications protocols used for the Internet and other similar networks. It is named one of the most important protocols in it: the Transmission Control Protocol(TCP) and the Internet Protocol(IP), which were the first two networking protocols defined in this standard.
IP:
It is responsible for moving a packet of data from node to node. IP forwards each packet based on a four-byte destination address (the IP number). IP operates on getways machines that move data from department to organization to region and then around the world.
TCP:
This is responsible for verifying the correct delivery of data from client to server. Data can be lost in the intermediate network. TCP adds support to detect errors or lost data and to trigger retransmission until the data is correctly and completely received.
Sockets:
It is a name given to the package of subroutines that provide access to TCP/IP on most systems.
Web site:
A Web page is a document, typically written in (X)HTML, that is almost always accessible via HTTP, a protocol that transfers information from the web server to display in the user’s web browser.
Home Page:
The main page of a website is called the Home Page. Typically, the home page serves as an index or table of contents to other documents stored at the site. In the following discussion, we will learn about some commonly used software like Operating Systems (A system software).
Operating System:
An operating system is like a mastermind program running on your computer. Every general-purpose computer needs one to get other programs going. OS handles all sorts of basic stuff, like recognizing what you type on the keyboard, showing stuff on the screen, keeping an eye on files and folders, and managing gadgets like disk drives and printers.
For large systems, the operating system has even greater responsibilities and power. It is like a traffic cop—It makes sure that different programs and users running at the same time do not interface with each other. The operating system is also responsible for security, ensuring that unauthorized users do not access the system. To visualize how an operating system works, refer to the below diagram.
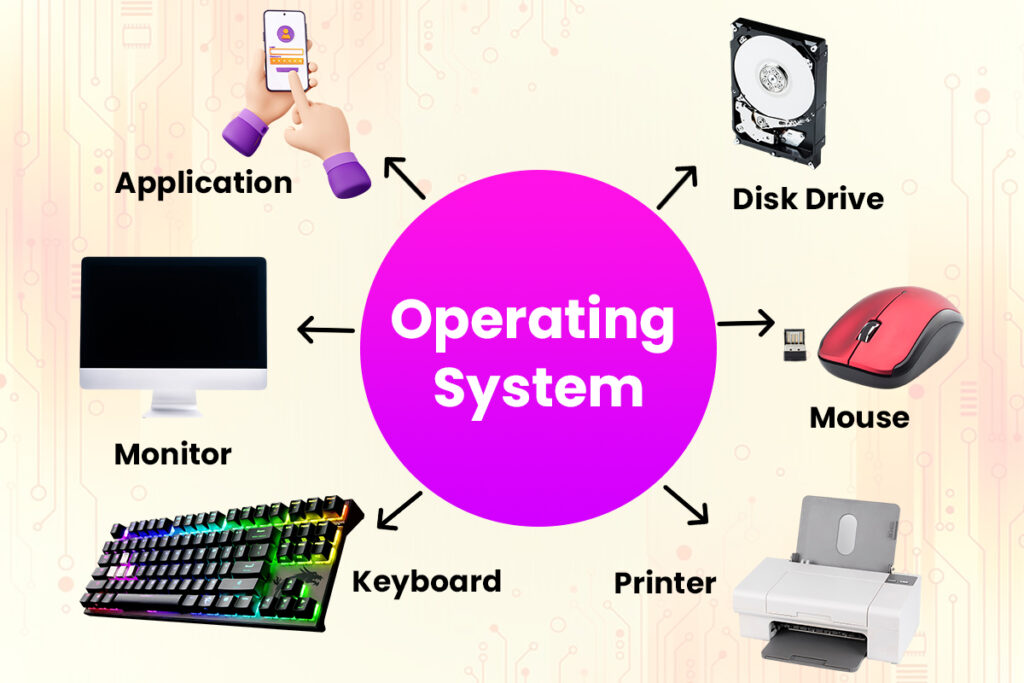
Operating systems can be classified as follows:
- Multi-user: Allows two or more users to run programs at the same time. Some operating systems permit hundreds or even thousands of concurrent users.
- Multiprocessing: Supports running a program on more than one CPU.
- Multitasking: Allows more than one program to run concurrently.
- Multithreading: Allows different parts of a single program to run concurrently.
- Real-Time: Responds to input instantly. General-purpose operating systems, such as DOS and UNIX, are not real-time.
What is Interface?
A User interface(UI) brings structure to the interaction between a user and the computer. Computer Interface is two types Character User Interface(CUI) and Graphic User Interface (GUI). In the last decade, almost all development in user interfaces has been in the area of the Graphical User Interface, with two models, Apple’s Macintosh and Microsoft’s Windows.
Character User Interface(CUI):
In computing, a character-based interface in which a prompt is displayed on the screen at which the user types a command. A typical example of a command line interface was the DOS prompt.
Graphic User Interface:
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is simply a method of interacting with a computer that uses pictures and text instead of just text. Like most things, some GUIs are better than others in certain areas. A well-made beginner GUI can make it easy for a new user to start using the computer to computer a task, and learn how to do new things on it. A powerful GUI allows an experienced user to do tasks quickly. A typical example of a Graphic User Interface is Windows.
Microsoft Windows:
Microsft developed the Microsoft Windows Operating system to overcome the limitations of its own MS-DOS operating system. The first successful version of this operating system was Windows 3.0, released in 1990. Subsequently, released versions were Windows 95, Windows 2000, Windows XP Professional, and Windows Vista.
Microsoft Windows is a Graphical User Interface(GUI). This screen appears when you start a computer—containing all the choices available to you. You interact with GUI using a mouse to move an on-screen Pointer. You choose an option by clicking the left mouse button once, sometimes twice in quick succession(a double-click). You can also use the pointer to mark bits of text or graphics that you want to copy, move, or delete, draw diagrams or pictures, move items on the screen, and carry out various tasks in different applications(i.e. programs).
Microsoft Windows is used by most IBM-compatible PCs. It does not run on the Apple Macintosh, which has its own quite similar, GUI.
Introducing to Windows XP:
The Windows Operating System started with the introduction of Windows OS and Windows for workgroup for networking. Since then it has come a long way and Windows 95, 98, and 2000 family of operating systems were introduced. It provided the computer user with the most integrated and easy-to-use operating system with all the facilities built. The Windows XP is the newborn baby in the Windows family. It is built on the Windows 2000 concept and framework. It has more features to provide the user with greater stability, security, and enhanced performance.
Editions of Windows XP:
The most commonly used editions are the Home and Professional editions.
Important Features of Windows XP:
Support long filename:
Supports long file names rather than the severely limited 8.3 character file names used by DOS. Windows XP supports file names up to 255 characters like other Windows versions.
PnP Feature:
Supports the new plug-and-play (PnP) standard being developed by PC makers that allow us to simply plug a new board (or interfacing card like a sound card, networking interfacing card, etc.) into our computer without having to set switches or make another setting like IRQ.
Windows Explorer:
Explorer is a special new feature that replaces the program manager and file manager features of the previous version and makes the multitasking feature easier for new users.
New Dialog Box- ‘Run’:
The run dialog box will allow you to run a program. For example, if we wanted to execute MS. Paint, therefore we typed “mspaint” in the run dialog box and clicked on OK to execute the program.
Access Previous Version Files:
Another great new feature allows you to access previous versions of files without even having a backup. This is possible through the volume shadows copy technology. If you want to do that manually, then you will have to use the file back wized in which you select the types of files you want to backup, specify a storage folder, and start the process at any point you want. There is also an automatic scheduling function.
Advanced OLE Feature:
Windows XP presents OLE(Object Linking and Embedding) which us to create more fancy documents combining information from several different applications.
Enhanced Message Controlling:
Supports a new mail system called Microsoft Outlook Express for managing all types of messages, computer users typically have to deal with E-mail, Internet Browsing, Netgroup receiving, etc.
Support Universal Serial Bus(USB):
A new peripheral connection lets you chain up to 127 devices such as digital audio and digital video cameras. We can also add or remove the device without turning off the monitor. That’s why USB devices are also called “Hot swapped”.
Support Multiple monitors:
Windows XP supports adding multiple monitors to your computer. This feature requires multiple PCI adapters.
